Buddhism is more than just a religion—it’s a way of life. At its heart, Buddhism teaches people how to understand suffering, let go of attachment, and walk a path toward inner peace and enlightenment. Instead of focusing on worshipping a god, Buddhism focuses on self-awareness, compassion, and wisdom. Think of it like a mental gym for the soul—train your mind, and the rest follows.
Origins of Buddhism
Buddhism began over 2,500 years ago in South Asia and slowly spread across continents like ripples in water.
Life of Gautama Buddha
Gautama Buddha was born as a prince in present-day Nepal. Sheltered from suffering, he eventually encountered old age, sickness, and death. These moments shook him awake. He left his royal life behind and went searching for truth—kind of like quitting a comfortable job to find real meaning.
Core Teachings and Philosophy
The Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path form the backbone of Buddhist teachings. They explain why suffering exists and how to overcome it through right action, right thought, and right living.
What Does “Buddhist Country” Mean?
Majority-Buddhist Population Explained
A Buddhist country usually means that more than 50% of the population practices Buddhism. It’s not about laws forcing religion but about cultural and social reality.
State Religion vs Cultural Influence
Some countries officially recognize Buddhism as their state religion, while others don’t—but Buddhism still deeply shapes daily life, traditions, and values.
Buddhism in Government and Society
In many Buddhist countries, monks are respected advisors, temples are community centers, and Buddhist festivals are national holidays.
How Many Buddhist Countries Are There in the World?
The Short Answer
There are 10 countries in the world where Buddhism is the majority religion.
Different Ways to Count Buddhist Countries
If you include countries where Buddhism has strong influence but is not a majority, the number rises to around 15–18 countries.
List of Buddhist-Majority Countries
Thailand
Thailand is often considered the heartland of Theravāda Buddhism. Over 90% of the population practices Buddhism, and monks are deeply respected.
Cambodia
Buddhism is the official state religion of Cambodia. Temples, or pagodas, are everywhere and play a major role in village life.
Myanmar
Myanmar has one of the highest percentages of Buddhists in the world. Monastic life is common, and meditation is widely practiced.
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is one of the oldest Buddhist nations, preserving Theravāda teachings for centuries.
Bhutan
Bhutan follows Vajrayāna Buddhism and is famous for its Gross National Happiness philosophy, which reflects Buddhist values.
Laos
In Laos, Buddhism shapes education, festivals, and everyday routines. Morning alms for monks are a daily sight.
Mongolia
After a revival post-communism, Buddhism has regained its central role in Mongolian culture.
Japan
While modern and high-tech, Japan remains culturally Buddhist, with Zen Buddhism influencing art, design, and mindset.
Vietnam
Vietnam blends Mahāyāna Buddhism with local traditions, making it a unique spiritual landscape.
South Korea
Buddhism coexists with Christianity and Confucianism but remains a core part of Korean history and identity.
Countries Where Buddhism Is Influential but Not a Majority
China
China has the largest number of Buddhists in the world, even though Buddhism is not the official or majority religion.
Nepal
The birthplace of Buddha, Nepal has deep Buddhist roots despite Hinduism being dominant.
Taiwan
Buddhism in Taiwan is vibrant, modern, and socially active.
Singapore
Singapore practices religious harmony, and Buddhism is one of the major religions.
Malaysia
Though Islam is dominant, Buddhism is widely practiced among Chinese communities.
Types of Buddhism Practiced in Buddhist Countries
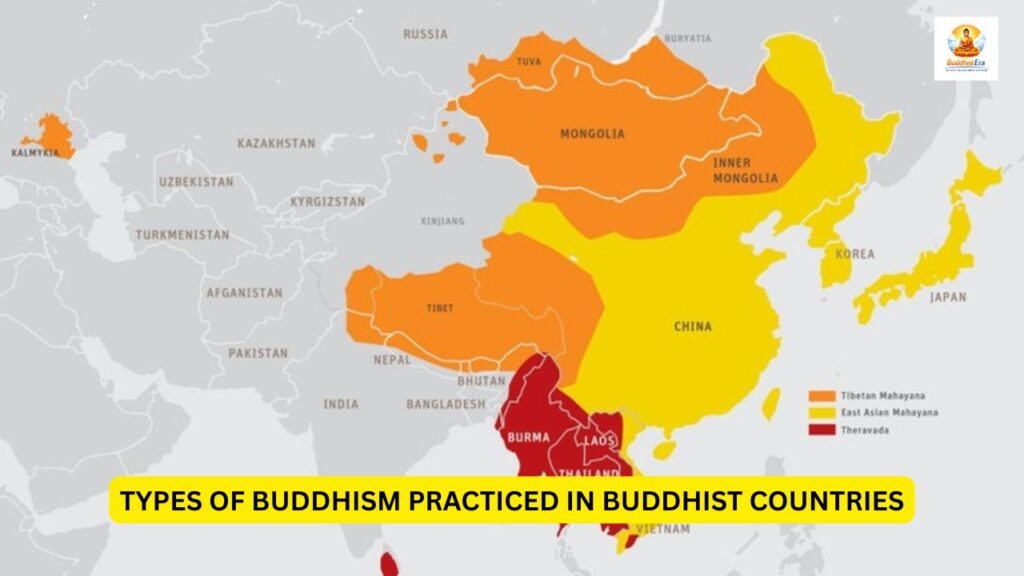
Theravāda Buddhism
Common in Southeast Asia, it focuses on original teachings and monastic discipline.
Mahāyāna Buddhism
Popular in East Asia, it emphasizes compassion and helping others achieve enlightenment.
Vajrayāna Buddhism
Practiced in Tibet, Bhutan, and Mongolia, it includes rituals, mantras, and meditation techniques.
Buddhism by Region
Southeast Asia
This region is the stronghold of Theravāda Buddhism.
East Asia
Mahāyāna Buddhism dominates, blended with local philosophies.
South Asia
Home to Buddhism’s origins and ancient heritage.
Central Asia
Vajrayāna traditions thrive here.
Why Are Most Buddhist Countries in Asia?
Historical Spread of Buddhism
Buddhism spread through monks, traders, and emperors like Ashoka.
Trade Routes and Empires
The Silk Road acted like an ancient internet, carrying ideas across borders.
Cultural Acceptance
Asian societies embraced Buddhism’s peaceful philosophy naturally.
Buddhism Outside Asia
Buddhism in Europe
Growing through meditation centers and mindfulness practices.
Buddhism in North America
Popular among people seeking mental clarity and balance.
Buddhism in Australia
Strong immigrant communities and modern spiritual seekers keep it alive.
The Role of Buddhism in Modern Buddhist Countries
Buddhism and Daily Life
From morning chants to ethical living, Buddhism shapes routines.
Festivals, Monasteries, and Monks
Festivals like Vesak celebrate Buddha’s life events.
Buddhism and Education
Many schools teach Buddhist ethics and meditation.
Is Buddhism Growing or Declining Worldwide?
Population Trends
While some regions see decline, global interest in Buddhism is rising.
Modern Challenges and Revival
Urban life challenges tradition, but mindfulness revives interest.
Common Misconceptions About Buddhist Countries
Buddhism Is Not a God-Based Religion
It focuses on self-realization, not divine worship.
Buddhist Countries Are Not the Same
Each country practices Buddhism in its own cultural flavor.
Cultural Impact of Buddhism on Countries
Art and Architecture
From pagodas to giant Buddha statues.
Meditation and Mindfulness
Now global trends rooted in Buddhism.
Ethics and Lifestyle
Non-violence and compassion guide daily life.
How Buddhism Shapes National Identity
Buddhism and National Symbols
Flags, emblems, and ceremonies reflect Buddhist values.
Buddhism in Law and Politics
Some laws are inspired by Buddhist ethics.
Future of Buddhist Countries
Globalization and Change
Tradition meets technology.
Preservation of Tradition
Monasteries and education keep teachings alive.
Read also:-
- Can Buddhists Eat Meat? A Complete, Honest, and Practical Guide
- How Many Buddhists Are in China? A Deep Dive into Numbers, History, and Reality
Conclusion:-
So, how many Buddhist countries are there in the world? The clear answer is 10 Buddhist-majority countries, with several others where Buddhism plays a powerful cultural role. Buddhism may have ancient roots, but its relevance today is stronger than ever—guiding nations, shaping cultures, and helping individuals find peace in a noisy world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How many Buddhist countries are officially recognized?
There are 10 countries where Buddhism is the majority religion.
2. Is China a Buddhist country?
China is not officially Buddhist, but it has the largest Buddhist population.
3. Which country has the highest Buddhist population percentage?
Thailand and Cambodia are among the highest.
4. Are there Buddhist countries outside Asia?
No country outside Asia has a Buddhist majority, but Buddhism is practiced worldwide.
5. What is the future of Buddhism globally?
Buddhism is expected to grow through mindfulness, meditation, and global interest.
